-
-
Supporting strategy-creation in the field of internationalization
HungaryDebrecenData-driven local governance aiming at improving the life of internationals

- Local economy
Copy linkFacebookXLinkedInEmail208 000Summary
In Debrecen, traditional approaches to economic development were mostly about developing infrastructure, rather than focusing on people. After moving to making data-driven decisions, via survey of needs, Debrecen has been able to develop a strategy to welcome and retain international talents.
Solutions offered by the good practice
Debrecen is the economic, cultural, and scientific centre of eastern Hungary – and the country’s second largest city. With a booming economy, the city allocates considerable resources to promoting international investment and developing local businesses. Recently Debrecen announced more than two billion euros in foreign direct investment and 8000 new workplaces.
Hosting several multinationals such as BMW, Continental and Thyssenkrupp, and one of the oldest and largest universities in the country, Debrecen has a fair amount of international talent – and employment opportunities. Several separate initiatives were available to help international professionals and students on arrival in the city and during their stay.
However, support was lacking in some areas. For example, many expatriates struggled to find suitable affordable housing, or understand key municipal information in Hungarian. Traditional approaches to economic development were mostly about developing infrastructure, rather than focusing on people.
Debrecen’s involvement in WIT was managed by the city’s economic development centre, the municipality-owned company EDC Debrecen Nonprofit Kft (EDC). To enable the municipal government to make data-driven decisions, EDC launched an initial survey to identify internationals’ needs.
Through interviews, and 450 survey answers for online questionnaires, EDC gathered perspectives on Debrecen’s safety, public transport and culture etc. The results showed that international residents appreciated the calmness, green areas, and social life, but lacked centralised information in English and international cultural events. Specific questions to international students also helped analyse potential future skills in the workforce and their match with the city’s growing number of multi-national corporations.
Sustainable and integrated urban approach
The aim is to create an environment, in which internationals find proper living conditions, that enriches the attractiveness of the city. The more international talent settles down in Debrecen, the higher the need for their integration is. Their expertise, skills and experiences help Debrecen reach a higher value-added in terms of economy, living conditions and social aspect.
This process and integrity are emphasized by the Welcoming policy of Debrecen in the framework of internationalization. This policy contributes to the development of Debrecen in the field of local business environment, tourism, education (from kindergarten till higher education) which supports the sustainable urban development.
Participatory approach
The URBACT Local Group (ULG) brought together stakeholders linked to the city’s Investment Strategy and others such as expat relocation services. This helped Debrecen to develop a new motivation to change the city’s mindset towards internationalisation – and played an important role in looking at how they could help make life easier for expats in their city.
Learning from Groningen and partner cities at WIT transnational meetings, EDC Debrecen developed a valuable peer learning approach locally, working with stakeholders individually on specific questions.
The strong stakeholder relations developed through WIT have played a key part in convincing local leaders to also focus on the social aspects of economic development. Building on this, EDC Debrecen will continue to pursue longer term goals, such as improving support for affordable accommodation, and encouraging local companies to recruit international talent.
What difference has it made
Given the linkages of the project to wider inward investment and economic development strategies, they engage with individuals on a one-to-one basis. The objective is to keep on growing the local economy and an integral to that is relationships with people, whether that be multinational companies, workers, or students.
Language was confirmed as a serious barrier for many internationals trying to settle in Debrecen. So, supported by the Vice-Mayor, the ULG and EDC Debrecen decided to develop a website in English with practical information on topics ranging from jobs and housing to cultural programs.
EDC Debrecen also identified other websites where English versions would be useful, for example on public transport, city works, the Christmas Fair, and other events. The local theatre started providing English subtitles, and other foreign languages will be introduced into the city’s cultural programme.
Transferring the practice
The long-term goal is to promote the internationalization of Debrecen, and to keep contributing to its urban and economic development. International presence in Debrecen makes our city a genuine multicultural community and enhances the achievement of the objectives we outlined in our Debrecen2030 Development Program. The city seeks to be as attractive as possible for international talent to stay and in our vision the city cannot be imagined without an international profile.
The base of the transferring journey was to change the mindset not only within our organization but among stakeholders and the municipality.
Emailvamos.mariann@edc.debrecen.huRef nid16283 -
A municipal farm to supply local canteens
BulgariaTroyanPaving the way for city leadership in local food production

- Climate action
Copy linkFacebookXLinkedInEmail33 500Summary
Troyan developed the first municipal farm of Bulgaria, with the aim to producing food for its school canteens. During 2.5 years, it got inspired by the Good Practice of Mouans-Sartoux which enabled empowering an already on-going transformation at city local level. In the long-run, 15 ha of publicly owned land, including 200 m2 of greenhouse tunnel will produce food for the 500 children in the town’s kindergartens.
Solutions offered by the good practice
Troyan is a town in the hills of central Bulgaria known for its strong plum brandy and with strong ambitions for its agri-food sector. Its 2014-2020 Municipal Development Plan already prioritised organic farming, support for young farmers, and conservation.
Troyan aimed at delivering fresh organic products to its school canteens and started working with a research institute to plan the development of organic fruit and vegetable production – including locally-adapted plum and apple varieties. To support this, in 2018, the town announced that 15 ha of publicly owned land would be dedicated to a municipal farm, with areas for vegetables, fruit trees and cattle grazing. Troyan joined the BIOCANTEENS network to help develop an operational process to carry this out.
Troyan’s municipal farm is the first of its kind in Bulgaria. To achieve this, the town took a step-by-step approach - initially aiming to provide half of the vegetables required in local canteens, then expand production later.
In March 2019, a meeting with Rozalina Rusenova, Deputy Mayor, confirmed the new farm’s overall infrastructure: three 200 m2 greenhouse tunnels, with an irrigation system and space for a fourth tunnel; and farm building facilities including a hall, storage space, refrigeration chambers and a preparation room for end products.
Whilst the pandemic and the cold 2019 winter slowed the municipal farm’s development, good progress has been made. Local farmer Maya Genkova was recruited to run the farm – including both production and educational visits.
Organic fruit orchards and first vegetables were planted in greenhouses at the end of 2020. These are expected to supply fresh organic fruit and vegetables to all 500 children in the town’s kindergartens during the course of 2021. Activities will also be organised for children on site.
The organic certification process was also launched with the National Food Agency - an essential step before serving the food in school canteens.
Sustainable and integrated urban approach
Troyan’s approach followed the main integrating axes of the good practice it was transferring, Mouans-Sartoux:
- Horizontal integration: by supporting smart land use, organic production and local agri-food systems development, the project has a strong environmental dimension. It also has an economic dimension through the creation of 1 farmer job. From a social aspect, the activities organised on the farm will enable raising awareness of children on local organic production and healthy eating. Production is 100% organic.
- Territorial integration: the project is totally integrated in the overall strategy of the city as owned by the municipality and directly linked with school canteens provisioning.
Troyan’s transfer process benefited from a particularly positive situation: the strong political involvement of Mayor Donka Mihaylova to improve the quality of city school canteens; no major financial barriers to set the farm, the city owning a provision of suitable land in a region with good assets for agriculture; a city canteens system relying on “traditional” independent kitchens organized to prepare fresh vegetables and fruits; a good mobilization from start of stakeholders in the ULG involving Heads of all city schools and kindergartens, civil servants and representatives of parents association; last but not least, a BioCanteens’ project that raised the enthusiasm in the local stakeholders ecosystem.
Participatory approach
This process was supported by an URBACT Local Group involving heads of all city schools and kindergartens, civil servants, parents’ association, local producers and representatives of children associations. During the course of the project, 10 ULG meetings with stakeholders’ involvement were held in Troyan. The main subjects discussed during the meetings were the Municipal Farm Platform, the Kitchen Micro-good practices and the organic demand and supply.
What difference has it made
- The Municipal Farm has been made with minimum resources;
- Children are provided with fresh organic vegetables and fruits’;
- The amount of money parents pay per month for daily kids food at the kindergarten was made cheaper;
With that difference of that payment, we invest in more quality products.
Transferring the practice
Troyan has been part of the BIOCANTEENS Transfer network led by Mouans-Sartoux (France) together with other 5 European cities LAG Pays des Condruses (Belgium), Vaslui (Romania), Trikala (Greece), Rosignano Marittimo (Italy), and Torres Vedras (Portugal).
The success of Troyan is in part due to a transfer process in the framework of an URBACT network arriving at the right time to boost and implement an ongoing policy orientation toward healthy and sustainable food in the city: this is certainly a lesson learned for URBACT transfer process who best apply when empowering an already on-going transformation at city local level.
Beyond the inspiration and guidance provided by Mouans-Sartoux, one of the most valuable network activities was a network workshop on public procurement. This helped Troyan understand what it is possible to achieve with the right plans, procedures and award criteria.
The transnational meeting hosted in the city itself in July 2019 also had an important local benefit in reinforcing support for the municipality’s agri-food strategy. The involvement of the Mayor Donka Mihaylova in this meeting was key.
While work with school kitchens and on the municipal farm continues to develop, Troyan is starting to apply new ideas and perspectives on Public Procurement to improve supply to school canteens. Further next steps include an initiative to support the preparation of meals inside school canteens, and expanding the supply of local, healthy organic food to the municipality’s elderly residents.
Emailpostbox@troyan.bgRef nid16282 -
Sharing stories in person and online to strengthen a suburban community
FinlandPoriCreating a place for mobilising citizens, fostering civilian power and urban stewardship through raising awareness towards the values of built heritage

- Urban planning
Copy linkFacebookXLinkedInEmail84 500Summary
Affecting the discourse on built environment and cultural heritage may have striking influence. Audio-visual documentation, storytelling and promotion via internet is a good way to raise awareness and bring visibility to places and people that are otherwise not under the radar of the decision makers.
Sharing stories of buildings brings about the dimension of time in living environment that helps in animating and enchanting the world and community.
Pori has applied the basic idea of the Budapest100 good practice in an innovative way (partly because of the restrictions of the COVID-19 pandemic), transforming an abandoned radio station in the eastern suburban location of the city into a Story Café which offers a cultural, creative and social space, reaching the locals and bringing them together to share stories.
Solutions offered by the good practice
Pori is an old industrial city on Finland’s West coast. The city selected an action area for the Come in! project in its eastern suburbs, which sprang up in the 1950s-1970s in proximity to a copper factory. The area is located 4km from the centre consisting of a park and the nearby residential areas, representing the main trends of post-war architecture in Finland. The park area remains unbuilt because of a shortwave radio station located in the middle, which is owned by the City of Pori and used since 2012 by a local artist community as well as an old vehicle club. With the permission of the city the artists operate the building as a creative space. In the last years, they have opened it to the public several times. Even so, there seemed to be a need for something, bringing together nearby residents, like the good practice of Budapest.
Pori has had various projects in the action area and it has offered funding numerous times to different NGOs to do projects, which resemble the Budapest100 good practice closely, there hasn’t been the level of integration and cooperation between different operators achieved, especially regarding the activating of the local population. All the elements and opportunities for adopting something like the good practice have been present but the impetus for it hasn’t manifested itself.
By 2020 the ULG felt ready to create a community festival highlighting the built environment of the neighbourhood, its character and stories, and introducing the radio station and its potential as a social and cultural space the people could claim as their own. Sadly, due to Covid, these plans had to be cancelled. Instead, a socially-distanced pop-up exhibition showcased the station's history in September 2020 and finally a two week long Story Café in May 2021 opened new spaces in the radio station for public and created a place for histories, stories and art to be shared.
As the society around came to a halt, organisers wanted a new digital approach to dealing with community and a way to highlight the built heritage. They decided to build a website for the history of the building and the local stories relating to it. Stories, photos and different kinds of historical material was crowdsourced with the help of social media, and collaboration with local radios and other media.
The local group members are committed to further develop the radio station and surrounding area into a shared space that brings people together to celebrate the built heritage and take part in active citizenship. The aim is with the development of the cultural use and the digital dimension of the radio station also to reach an audience beyond the boundaries of Pori and Finland.
Sustainable and integrated urban approach
As the city itself has become more aware of the station thanks to the community activities, an interest in its development has grown significantly. Using built heritage to draw attention to a peripheral area succeeded since the municipality started to renovate the radio station and involve the area to the city-level participatory agency project. So, the usage of built heritage helps to gain tangible and visible results that can be communicated both on site in the neighbourhood and online to wider national and international audiences. Many further local actions have been initiated by the community engagement around the area:
- The Väinölä school with over 280 pupils decided to take the area and its multidisciplinary investigation as a theme for the whole school year 2020-2021
- Raised awareness of the international architectural value of Himmeli elderly house
changed the discussion on how to treat the building during its renovation, after a lecture by architect Juhani Pallasmaa (organized by the project coordinator of Come In!) on the heritage of architects Reima and Raili Pietilä who designed Himmeli
- In the end of 2020 the city ordered a master plan for the park area from one of the leading companies in Finland designing smart cities
- Best experts of Finland and students from the Aalto University School of Art, Design and Architecture from Helsinki carried out a full professional standard historical report on the radio station in May 2021. It will be published in summer 2021 working as a guide book for treating the building as a valuable piece of Finnish, European and global cultural heritage.
Participatory approach
For the local coordinators, this building and its surrounding green area seemed like an unused connecting tissue between the suburbs – an urban green space full of history and legends to be discovered to stimulate community spirit.
They built a website to be a platform where not only the official history and unofficial stories and legends, but also the present and ideas concerning the future of the radio station can be shared
The new place means new opportunities also to integrate migrant communities which live in the surrounding suburban locations.
What difference has it made
Too early to say – the place is just now in the process of opening due to the delay caused by the pandemic.
In January 2021 over 600 square meters of new space for culture, art and social gatherings was freed from the radio station when the car club moved away. The same area is part of a new national suburban development project (2020-2022) which offers also investments in infrastructure and so gives sustainability and continuity for the efforts of Urbact.
In May 2021 the Story Café concept proved to be a success with over 750 visitors during two weeks. It demonstrated very well, that a cultural, creative and social space is a very good idea and it has to be developed as well as the overall cultural use of the building.
Transferring the practice
After being awarded the URBACT Good Practice title, Újbuda was able to create the Come In! Transfer Network to which six European cities (Gheorgheni RO, Forlì IT, Varaždin HR, Pori FI, Plasencia ES, Targówek/Warsaw PL) were invited. Equipped by URBACT with a toolkit, the cities could learn from each other. The transfer process was not one-sided, during the transnational meetings the existing practices of some of the transfer cities inspired Újbuda and contributed to the development of ideas to further improve the Good Practice.
At first sight the case of Pori is different from the original practice, insofar it uses a stable place to activate residents from surrounding areas, offering for them new cultural and leisure opportunities. On the other hand, the methods to be used to get the place accepted, are very similar to that of the Budapest100 good practice.
Emailniilo.rinne@pori.fiRef nid16281 -
Experimenting with new types of grants in deprived areas which are not eligible for social funding anymore
FranceLilleFurther develop the area-based policy for deprived neighbourhoods by applying innovative elements in territorial sense, involving new types of local stakeholders and experimenting with new empowering methods

- Urban planning
Copy linkFacebookXLinkedInEmail1 068 000Summary
Lille aimed to transfer the Grant element of the Lisbon good practice, improving its own system, applied in the framework of the French urban policy. The introduced innovations refer on the one hand to the territorial choice, and, on the other, on the way how the grants are applied.
Instead of the most disadvantaged priority districts, the new Lille approach focuses on some active monitoring district (former priority districts which have lost this status due to improvement of indicator values) which are isolated, far from any priority districts. Such areas, as the municipalities of Lomme and Haubourdin, experienced a cut of tax benefits from the national state and from other institutions or agencies. Thus it has proven to be difficult to maintain the dynamic without coordination and support from the municipality.
Many diagnosis showed that the usual forms of call for proposals are very competitive, almost excluding the needed cooperation of stakeholders. Lisbon’s call for proposal system requires at least two entities to respond which enhance cooperation in neighborhoods. But call for proposals might not be the best tool to that purpose as it focuses on money issues, while many initiatives need other types of support such as loan of premises or equipment, skill sponsorship… As a consequence, Lille was looking for other methods to offer institutional help to the stakeholders through design thinking.
Solutions offered by the good practice
As a former major textile manufacturing centre, despite its success in economic restructuring, the Lille area has failed to balance the ongoing decline of manufacturing employment. Inequality within Lille Metropolis is greater than in any other major French cities, except for Marseille. Wide neighbourhoods suffer from severe long-term unemployment, urban decay, population decline, poor health conditions and welfare dependency.
Lille Metropole’s existing grant system is framed by the national urban policy, implemented through “City contracts”. Based on political decisions for six years at inter-municipality scale, the city contract is implemented through annual calls for proposals. Non-profit organizations, such as public institutions and NGOs, are invited to submit proposals for projects concerning the identified priorities.
Sustainable and integrated urban approach
French urban policy is area-based. The priority districts are defined by the national state on the basis of inhabitants’ low-income criteria (concentration of populations having resources lower than 60% of the national median reference income). There are 21 priority districts in the Metropole gathering 18% of the Metropole population. It’s the largest proportion among France’s big cities.
Furthermore, 20 areas in Lille Metropole are active monitoring districts which do not fit with the new priority districts’ criteria (the low-income rate or the concentration of population) anymore and are part of a less subsidized transition phase. Active monitoring neighbourhoods are no longer eligible for tax benefits and specific aids owed to priority districts. For example they are not qualified for national aids of the urban policy annual call for proposal.
Lille decided to focus on active monitoring districts which are isolated, far from any priority districts – in such areas it is difficult to maintain the dynamic without coordination and support from the municipality. As pilot the municipalities of Lomme and Haubourdin have been selected.
Participatory approach
Participation has always been one of the pillars of the “politique de la ville” policy. It is identified as one of the main conditions to secure the implementation of the city contract. It is a major challenge for Lille Metropole to increase the interest for civic participation, community life and endogenous development.
What difference has it made
The main ambition of Lille Metropole was to transfer the Grant system element of the Lisbon Good Practice. A new experimental Grant (Call for project) was aimed for, based on the Lisbon experience, finding new stakeholders to be involved, mobilizing more private investments in the priority neighbourhoods and to share new social innovation experiences. Lisbon’s good practice is seen as an inspiration to improve the Lille local grant system on the following points:
- Encourage cooperation between a various range of stakeholders in the neighbourhood (requiring responses by at least 2 different organizations)
- Attract new partners in the neighbourhoods, to draw more partners from the private sector, groups of inhabitants, other NGO’s…
- Promote a more participatory development, by enabling informal groups of inhabitants to participate in the projects
- Foster projects that can reach financial sustainability
Lille Metropole was chosen to be the World Design Capital in 2020, allowing for a year-long city promotion programme to showcase the accomplishments of cities that are effectively leveraging design to improve the lives of their citizens. Within this framework a labelled design service contractor could be involved as URBACT expertise.
In the course of work it became clear that the traditional system of ‘call for proposals’ has to be modified. To enhance the cooperation of the stakeholders the innovation of Lisbon’s call for proposal is applied (at least two entities have to respond which enhances cooperation in neighbourhoods). In order to strengthen qualitative elements, need for other types of support than money, such as loan of premises or equipment, skill sponsorship, other methods are experimented to offer institutional help to the stakeholders through design thinking.
Instead of simple call for proposals the question is raised: what does your area need? A kind of project factory is organized (the intervention of Francois Jegou), through organizing local workshops, listening to people’s ideas.
Recently the workshops are going on. ComUnityLab gave a starting point, now a new dynamics has been created which will last for 2 more years. Then the method will be distributed to other areas of MEL with precise conditions, how many organizations have to be included.
Transferring the practice
Lille was one of the seven European cities (besides Bari Italy, Aalborg Denmark, Sofia Bulgaria, Ostrava Czech Republic, Lublin Poland, The Hague Netherlands) of the Com.Unity.Lab Transfer Network, led by Lisbon, to transfer the URBACT Good Practice of Lisbon on the integrated toolbox for deprived neighbourhoods.
Equipped by URBACT with a toolkit, the cities could learn from the good practice and also from each other.
Emaillretournard@lillemetropole.frRef nid16280 -
Creation of a new NGO platform
SloveniaIdrijaThe new ‘Towns’ Living Room’, established by the municipality in a vacant building, involves the heads of the city administration, active citizens, social services, development agency, public library and nursing home, local clubs and various associations
- Social cohesion
- Local economy
Copy linkFacebookXLinkedInEmail11 800Solutions offered by the good practice
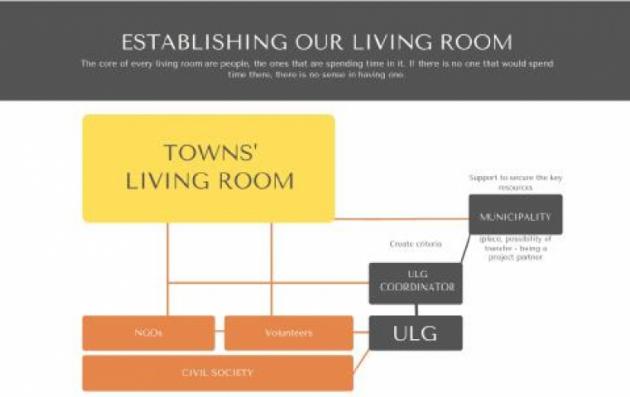
Fostering the engagement of inhabitants who are not in paid employment but have access to skills and resources to help support those in need, builds the capacity of civil society to engage with often complex social problems in a structured way. Altena founded its NGO platform in 2008 and called it Stellwerk. The Stellwerk started without a budget. The municipality made available premises, paid the energy and cleaning bills, provided a minimum of administrative resources. Currently the Stellwerk has 8 volunteer workers who co-ordinate several hundred volunteers providing disability support, arts and music groups, home visiting and home care services, refugee integration and much more. The Stellwerk provides an essential channel of communication between civil society and municipality.
In February 2020, Idrija launched its new ‘Towns’ Living Room’: the municipality offered a vacant building to house a small ULG involving the heads of the city administration, active citizens, social services, development agency, public library and nursing home, local clubs and various associations.
The ‘Towns’ Living Room’ links organisations with interested citizens if needed, but it is a “by the people for the people’’ model. Activities have already included events on housing and building refurbishment, chess classes, evening of poetry, book presentation, reading of fairy tales for children, knitting evening to raise breast cancer awareness and many more. It hosts services, such as a municipality supported volunteer based free transport service for elderly people and a book corner provided by the local library.
Sustainable and integrated urban approach
For successful transfer of good practice, it connected and established cooperation across different departments of a municipality. As well as also it strengthened the connection between local actors, NGOs and municipality.
With the practice based on ‘people to people’ approach it also improves the quality of design and implementation of smaller local actions.
Good practice works when there is trust established between all different parties – municipality, NGOs/volunteers, institutions and citizens.
Participatory approach
The practice is based on people, NGOs, volunteers that are encouraged by ULG. The coordination between all the elements was done by ULG coordinator. It includes all important stakeholders and interested citizens which is essential part of success of a practice based on ‘’people to people’’ approach. It uses bottom-up approach which leads to that people actually want to be part of good practice and want to give to community because they are having opportunity to fulfil their wishes and they actually have a say in what will happen.
What difference has it made
After official opening of the premises of the NGO platform (the "Towns living room’’) volunteers started to turn up. Ideas are coming in all the time which means that people are actually engaging and doing things on their own. There is also a wide acceptance now in public. At the start there were a lot of opinions about "just another project’’ and now those opinions are different and more in a way "we really needed that’’ "it is nice to have a place where we can do something’’. A lot of ideas are already on the list to do, and everyone is more confident now. With less Covid-19 restrictions the "Town living room" was able to open up again which resulted in a rich monthly program with different activities organized as well as giving people a place to hang out a bit without organized activities.
Transferring the practice
Idrija was one of the seven European cities (besides Manresa Spain, Igoumenitsa Greece, Isernia Italy, Melgaço Portugal, Aluksne Latvia, Nyírbátor Hungary) of the Re-grow City Transfer Network, led by Altena, Germany, to transfer the URBACT Good Practice of Altena on finding opportunities in declining cities. Some of the cities were transferring the NGO platform while others the Pop-up shops.
This good practice has also been chosen as one of 5 URBACT National Practice Transfer Initiatives (NPTI) and will be transferred to 6 other Slovenian municipalities. The project is led by Slovenian NUP, with Tina Lisac as national expert.
Equipped by URBACT with a toolkit, the cities could learn from the good practice and also from each other.
Re-grow City deliberately focused on small and medium sized towns, because they face distinctive challenges in terms of constrained resources and limited technical capabilities when compared to larger cities. These constraints offer opportunities, however, for example robust social networks with high levels of ‘social capital’ and short decision making routes that speed up the adoption of untested or controversial methods. Taken together with the resources and skills local people have, shrinking cities are places of opportunity and can demonstrate considerable resilience even where they face severe constraints.
As a side-outcome of the Re-Grow City network, in May 2021 the new pan-European network ReGrow Towns has been established. This is aimed for towns below the size of 50 th residents and is an addendum to the already existing networks of Eurocities (cities above 250 th residents) and Eurotowns (cities between 50-250 th residents).
Emailtina.lisac@icra.siRef nid16279 -
Building municipality- NGO cooperation
ItalySiracusaA new ecosystem of spaces for public-civic cooperation

- Participative governance
Copy linkFacebookXLinkedInEmail122 000Summary
The city of Siracusa has created a new ‘House of Associations and Volunteers’ transferring the practice of of the city of Riga leading the ACTive NGOss Transfer Networks, and a comprehensive governance model that sees as protagonists the local NGOs and the municipality, by boosting the uses and linking three civic spaces located in strategic locations in the city.
Solutions offered by the good practice
Through the experience of ACTive NGOs, Siracus succeeded to organise the co-management of new social aggregators regulated by a Protocol of Understanding among the Municipality and 27 associations active in the city.
Siracusa is a medium-sized city on the east coast of Sicily. With its rich ancient past, the city is listed by UNESCO as a world heritage site. Its main economy is tourism but its population suffers from under investments on utilities and infrastructure due to public budget cuts on social services, and endemic unemployment especially hitting the youngest population and migrants. In order to address some of these issues, the municipality wanted to cooperate more closely with various social and economic actors, and involve NGOs in promoting social inclusion and citizen participation. However, NGOs had limited opportunities and needed better physical spaces to carry out recreational, cultural and social activities, training courses, and citizens’ services.
In this frame, Siracusa wanted to experiment locally the Riga practice of the NGO house. Riga’s relied on substantial public funds for its large structure and dedicated staff, but this was not the case for Siracusa, which then decided to adapt the Riga example starting from the local resources. These were the three, already existing but dormant, civic spaces needing better management.
The solution is therefore a formalisation, through a “Protocol of understanding”, of the common use by NGOs of these under-utilised civic spaces:
- The Citizens’ House, a social center in the periphery of Siracusa, called La Mazzarona. The Citizens’ House was first established in 2015, after the city of Syracuse decided to join the GeniUS! URBACT II Transfer Network. La Mazzarona district presented many challenges, including high levels of unemployment, social exclusion and poverty. At that time except from a school, no services were available for the neighborhood’s residents. Public participation was for the first time activated in La Mazzarona thanks to the GeniUS! project, but the project encountered a halt which have been revitalised through the project House of Associations and Volunteers resulting from the ACTive NGOs URBACT III network.
- The Officina Giovani, (Youth Lab) located in the historic center of Ortigia, a space inaugurated in 2015 dedicated to aggregation and participation of the city’s youth.
- The Urban Center, located in the nineteenth-century city center, a space newly restored dedicated to citizens and local associations. Because of the Covid-19 pandemic the Urban Center has been temporarily converted into a Covid-19 vaccine location.
The three civic spaces are meant for organizing seminars and workshops, laboratories, events and thematic talks to address societal issues.
Sustainable and integrated urban approach
The case of Siracusa shows three main aspects of sustainable integration as intended in URBACT.
The first aspect is the vertical integration (the cooperation between all levels of government and local players’ among municipal sectors), a salient feature of this Siracusa case. The cooperation among the municipal administration and local associations, sharing ideas and objectives for the House od Associations and Volunteers is an important milestone considering that this form of cooperation was not experimented before. Through ACTive NGOs the local associations started to get to know each other, imagining new possible synergies while changing their position towards the local administration: from bodies mostly depending and benefitting from the public budget towards active subjects proposing, sharing visions and collaborating for better service provision. This reduced dependency from the public administration, the sharing of responsibilities by NGOs in the project is also a promise towards the self-sustainability of this practice.
The second is the territorial integration: the three NGO houses centers’ locations represent the decision of creating a spatial ecosystem that could cover the whole city.
The third is the combination of soft and hard measures by investing in refurbishing and ameliorating existing structures, combined with the investment on socio-cultural and inclusive activities.
Participatory approach
From the earliest stages of the project, participation has been essential. Looking at the experience of Lead Partner Riga, in 2019 an ad-hoc multi stakeholder URBACT Local Group (ULG) was created made up of municipality representatives and 27 associations active in the city. The ULG intensively worked with more than 15 meetings. This process of exchange led to a co-designed and co-written Protocol of Understanding to manage what is now in Sicuracusa called new Houses of Associations and Volunteers (Casa delle associazioni e dei volontari), signed by ULG members. The Protocol “defines the places, responsibilities and governance of a system made of the three Houses of Associations and Volunteers,” explained Caterina Timpanaro, an expert who supported Siracusa in the process. After signing the protocol, the associations elected their governing bodies and began to operate autonomously.
With this the municipality is learning the new role of supervisor, dedicating exclusive structures to associations, while listening to the needs to various stakeholders incorporating them into public programs and activities.
What difference has it made
The ACTive NGOs Network has given the opportunity to experiment a mode of cooperation of public and private sector creating new and effective synergy between the municipality and NGOs. The creation of a Protocol of Understanding is the tangible results establishing this collaboration to which local actors will refer to beyond the lifetime of the URBACT ACTive NGOs network:
The immediate next step for the municipality and local associations is to plan an innovative grand opening with residents, pending appropriate Covid-19-related arrangements.
In the longer term, Siracusa’s challenge will be to establish more structured cooperation between institutions and NGOs to change the nature of local services, based on a systematic involvement of citizens and associations.
Transferring the practice
Transferring Riga’s good practice meant to adapt the city’s trajectory to Siracusa’s particular history, driving forces and inertia in public-civic cooperation: in contrast with Riga’s fully municipality-financed and managed NGO House, in Siracusa the municipality provided the three civic spaces and then decided to step back and collaborate with local associations to co-develop and manage their spaces. The associations in fact elected their own governing bodies and began to operate autonomously from the municipality.
As an ACTive NGOs partner city, benefited from sharing methodologies, tools and knowledge from the other network cities. As examples Siracusa learnt the value of stakeholder “mapping” as an effective tool in the short and long term, helping improve and expand the knowledge from Santa Pola (ES) and has been inspired with new ideas for recreational activities (morning coffee, football matches, etc.) fundamental both for the ULG's commitment and for the activities with the residents from Brighton (UK). Dubrovnik (HR) proved that public administrations can use physical resources to create strategic locations and channel various funds, which Siracusa found “very inspirational”.
Emailnunzio.marino@comune.siracusa.itRef nid16278 -
The Altona Declaration: Making Inclusion and Tolerance Loud and Clear
GermanyHamburg-AltonaCo-creating a commitment to inclusion and tolerance

- Social cohesion
Copy linkFacebookXLinkedInEmail1 845 000Solutions offered by the good practice
Hamburg consists of seven districts and the district of Hamburg-Altona is the westernmost urban borough of Hamburg with a population of 270, 263 (Dec. 2016) with an area of 77.4 km2. The District of Altona is therefore part of the greater City of Hamburg, a major trading crossroads on the North- as well as Baltic Sea with both a long history of immigration and a growing, diverse population. Around 14% of the city’s residents are from first or second generation immigrant backgrounds, a statistic of foreign population growing in the district of Altona.
Between 2015-16, 60,000 refugees arrived in the city requiring the provision of extra accommodation and services and Hamburg employed some innovative processes to do this such the “Work and Integration Centre for Refugees – WIR-Centre” the Finding Places scheme- URBACT recognised Good Practice. A large proportion of refugees have been accommodated in Hamburg-Altona.
However, in recent years, the city has witnessed a disturbing rise in xenophobic populism and hate speech in both traditional and social media. Preoccupied for the phenomena, and for the attack of public opinion towards a pro-refugees agenda of the city of Hambourg, the District of Altona in 2018 analysed the situation in paper on integration and social inclusion. This paper led to a revision and updating of the local strategy from integration of minority groups (Integrationskonzept), towards comprehensive policies of inclusion and diversity targeting the whole population. While politicians were generally committed to this approach, they soon perceived the limits of issuing a top-down agenda in favour of tolerance and diversity., which would have been perceived by locals as imposed.
The solution evolved by joining the URBACT Transfer Network of Rumorless cities towards co-designing with inhabitants a formal declaration of inclusion and a campaign in public space about the principles exposed in the declaration. At first, public events and workshops have been organised across the district and via digital communications, inviting residents from different backgrounds to share their opinions on concepts such as social cohesion, community, democracy and equality and what sort of society they want to live in.
In the second phase, the content collected during phase one was collated and edited into seventeen statements. These were promoted at summer festivals across the district and people were encouraged to vote, to which 1 000 people responded. Subsequently, the declaration was launched at a press conference by the city mayor and by Marcell Jansen a famous local sportsperson. This was closely followed by a public democracy conference with the goal of supporting citizens to make the declaration their own and to develop ideas for spreading it’s messages and values. The declaration turned then into a campaign with printed and digital media in public spaces. Unfortunately, Covid-19 was tough for a campaign so strongly reliant on face-to-face activities. The work with schools was stopped, and Altona’s biggest cultural festival — potentially a powerful catalyst for promotion — was cancelled. This forced a creative rethink and a shift towards digital communications, including a campaign kit for civil society organisations.
Thankfully, the Mayor of Altona was personally committed, speaking at the launch event and referring back to the declaration in a public statement condemning discrimination after hate mail was sent to the Altona mosque.
Sustainable and integrated urban approach
Altona practice focuses on integrating the good practice of Rumourless cities across departments in the district offices and involving local population in co-designing the antidiscrimination campaigns that involves not only minority groups but the whole population. Altona is committed to exploring further ways to communicate and embed the declaration in the life and institutions of this district of Hamburg. For example, politicians have agreed to display a plaque of the declaration prominently on the town hall. A crucial target group is now schools and young people who will be invited to visit and discuss the values and ideas set out in the declaration.
Participatory approach
In Altona, a group of stakeholders was already co-developing an anti-discrimination strategy, including a set of principles to be known as the ‘Altona Declaration’. Joining URBACT RUMOURLESS CITIES Network was a chance to add inspiration and momentum to this campaign, and transform the initial idea of a top down anti-discrimination campaigning into a co-designed strategy (see Solution section). The existing stakeholder group in Altona formed an expanded URBACT Local Group (ULG), bringing political leaders and residents.
What difference has it made
The collaboration among inhabitants and city offices to co-create the Altona Declaration resulted in a series of 17 anti- discrimination statements posted online and promoted at events. 1000 people voted, selecting the top seven statements that formed the body of the declaration now part of a larger campaign involving public spaces in the district. The local partners and especially the ULG-members used the new kit, eg the flyers and posters, to disseminate the seven thesis of the Altona Declaration.
The change of attitudes is not easy to measure, especially not with the resources of the project. But one can be hopeful that some, more doubtful persons, started to reflect their personal points of view on diversity.
”In concrete terms, we were able to benefit from the exchange with the international partner cities. We learned how great the influence of positive rather than negative framing can be in conveying messages”. Adelina Michalk Department of Social Services, Municipality of Hamburg-Altona.
Transferring the practice
Hamburg/Altona found the regular peer review opportunities during transnational meetings of the Transfer network Rumorless cities particularly useful for taking on board practical tips and ideas for anti-rumour strategies. This included a ‘Gallery Walk’, where partner cities used visual images to capture their progress and exchange learning.
One notably valuable technique transferred from the city of Amadora, lead partner of the Transfer network, was the active involvement of ‘ambassadors’ to convey key messages to sections within the community. These elected officials, civil servants, and influential citizens assumed a pivotal role as the local campaign was rolled out.
Emailadelina.michalk@altona.hamburg.deRef nid16276 -
Music for social change in Brno
Czech RepublicBrnoShaping inclusive public education through performative arts

- Social cohesion
Copy linkFacebookXLinkedInEmail381 000Solutions offered by the good practice
Brno, the second largest city in the Czech Republic, despite a low poverty rate overall, has identified 16 areas at risk of social exclusion. Mostly located close to the city center and populated by 12-15 000 citizens, these areas are home to mainly Roma people – the major ethnical minority in Brno. Experts estimate that 78% of Roma children leave school early, compared with a regional average of 2.7%. To deal with this situation, Brno municipality welcomed the proposal of the URBACT network ONSTAGE transferring the good practice of L’Hospitalet, namely of the Municipal Music School and Arts Centre (EMMCA) , an education scheme that improves social inclusion through arts and music. Even before ONSTAGE, the municipality co-financed a music programme provided by local organisations and ran high-quality affordable music schools (ZUŠ) for children throughout the city, but children from socially challenged backgrounds were usually unattending.
Through ONSTAGE a wide variety of stakeholders, including representatives from the municipality and the region, all local non-profit organizations and schools situated in the target areas have been brought together to introduce the educational music program similar to EMMCA’s one in 10 target schools.
Brno’s pilot program began in September 2019 in the primary school ZŠ nám. 28. Října, extending the morning curricular programme with an extra music lesson for 5th to 9th grade classes. In parallel, another music program was started in a newly opened kindergarten, MŠ Sýpka, which entailed the setting up of a weekly group music course and the purchase of musical instruments.
At the end of November 2019, a free-of-tuition community choir ONSTAGE was established. In January 2020, another music program in the primary school ZŠ Merhautova (3x2h/week) was opened.
In the spring of 2020, all the programs were well established, but encountered a halt during lockdown. However, despite the slowing of activities due to Covid-19, group violin, cello and guitar lessons began in two primary schools — and in September 2020, 37 students signed up for guitar lessons, four times more than the year before. As a result, the project had a real impact on the understanding and use of music for social change.
Sustainable and integrated urban approach
One of the key points of the approach has been the establishment of the Urban Local Group (ULG), composed by a wide variety of stakeholders, including both institutional representatives (from the municipality and the region), local associations, and schools. This alliance has been fundamental in supporting the project throughout its duration and assuring the project’s sustainability after its official conclusion. The diversity of the ULG’s members also meant valuable insights into the specific problems of social exclusion and policies to counteract them from different perspectives.
Participatory approach
Participation has been one of the main objectives of the project since its early stages and there are now a lot of agents positively engaged.
By targeting schools with a high number of pupils from socially excluded segments of society, participation in the music programs has been fundamental in bringing together children from different backgrounds.
The choir represented an important tool for participation as well. It was the result of a cooperation with local non-profit organization IQ Roma Servis and it was free of tuition. At the basis of the project there was the belief that a broad repertoire – popular songs, gospels and traditional Roma songs – and no age restriction represented promising concepts for creating a community space where local people could meet and share the joy of making music together and get to know the richness of the Roma’s musical culture.
What difference has it made
The ON STAGE Transfer Network has made it possible in Brno to think of an innovative and more inclusive music education system through enhancing social cohesion.
Although state basic schools (ZUŠ) offer high quality music education, it is mainly designed to prepare students for the conservatory, which opens for them the opportunity to pursue a professional career in music. Teaching music to enhance social cohesion was a concept little known in the city and its potential had hardly been explored. Being part of the ON STAGE project gave Brno the chance to change this. Social cohesion has been enhanced and many children who did not attend musical classes before have then joined the new programs. For the second year of the programme (2020/2021) even more people signed to the courses and the choir.
Despite Covid-19 related restrictions, all the programs have been successful in establishing foundations with students and teachers who believe in the idea of the project and are willing to continue. In only a short period of time, the ON STAGE project has been meaningful for Brno and can actually make positive changes.
Transferring the practice
The ON STAGE Trasfernetwork was led by the city of L’Hospitalet and involved, apart from Brno, Aarhus (Denmark), Katowice (Poland), Adelfia (Italy), Valongo (Portugal) and Grigny (France).
The ON STAGE Transfer Network organized also a teachers’ mobility program. For Brno’s teachers, seeing L’Hospitalet’s group-based ‘El Sistema’ teaching method in practice was a real eye-opener — as were opportunities to exchange with partner cities such as Grigny (a suburb of Paris, France).
Emailbarickmanova.andrea@brno.czRef nid16273 -
Let’s Play Cork
IrelandCorkExperimenting, improvising and evolving playful strategies to improve the lives of our citizens

- Urban planning
Copy linkFacebookXLinkedInEmail125 622Solutions offered by the good practice
Cork is Ireland’s second largest city, and a busy port, a hub of industry, located in the south-western corner of the country. URBACT Playful Paradigm Network, ‘play’ for Cork City Council was predominantly about the construction and management of playgrounds. A holistic understanding of play did not exist beyond a handful of practitioners. Learning from Udine meant adapting the god practice and inventing new project that could respond to local constraints such as the challenge to organize public events due to legal requirements for public liability insurance, or lack of resources as for the ludobus project.
The creativity of the URBACT Local Group led to the creation of a new figure, the part-time Play Development Officer and 26 certified volunteer ‘Play Leaders’, which developed a wide range of projects such as:
- Toy Libraries: in Cork there are ten municipal libraries throughout the city. Thanks to the Network, members of the City Library and a member of Young Knocknaheeny, a group that specializes in early childhood development, had the opportunity to do a study visit to Paris and see how a Toy Library works. They came up with the idea to store “Community Play Bags” in the ten municipal libraries. The “Community Play Bags” are oversized sports gear bags containing equipment for cooperative play, which is appropriate for different ages. By placing them in the library system, the project has been developed to allow for borrowing by community-based organizations seeking to incorporate play in their activities.
- Playful Placemaking The Marina is a road of approximately 2.5 km along the River Lee in the city. This road was mainly used for car traffic, yet it had potential as an amenity for outdoor recreational activity and for the general enjoyment of the river. The Cork project team decided to test two project actions namely to organize a playful festival and some pop-up play events by applying to stop car traffic on the Marina road for car traffic on four Sundays in the summer of 2019. The communication was not on ‘closing the road’ per se, but rather on opening the road for play. This was done as part of the city’s annual Lifelong Learning Festival.
- Ludo buses inspired by the lead partner Udine’s good practice, Cork has developed its own Ludo Buses. Ludo buses are vehicles that contain outdoor games that can be driven to any public space/gathering and made available to the community as a play resource for a number of hours.
- Play Packs With the disruption of Covid-19, the Cork City Council’s Social Inclusion Unit teamed up with the community and voluntary sector to create Play Packs. They contained booklets, video-tutorials and materials to create games at home, such as lollipop sticks, colouring pencils and crayons) and were distributed to hundreds of families in need during the first period of the Covid emergency. The Play Packs created a buzz in the local community and were seen as a useful tool also for other disadvantaged categories. Cork recently decided to start a new wave of distribution to people with intellectual disabilities and to people living in nursing home and long-stay hospitals.
Sustainable and integrated urban approach
The project of Cork has predominantly invested into soft measures for social inclusion, promoting the integration and collaboration of different actors both across different departments of the municipality with diverse and multi sector group, called “Let’s Play Cork”, coordinated through Cork Healthy City (Cork is in fact in the World Health Organization “Healthy Cities” network since 2012) and Cork City Council along with members of Cork City Libraries, Young Knocknaheeny (a group that specializes in early childhood development), Foróige (a charity which addresses youth development), Cork Lifelong Learning Festival and Meitheal Mara (a community boatyard in Cork). The scope has been to foster a play-oriented approach to education and public space management in the city.
In terms of sustainability the city has continually sought seed funding from alternative sources to make Let’s Play Cork continue after the end of the Transfer Network. The city is also looking at specific investments based on the lessons of the project. Notably, the City Council has earmarked the riverside road for a EUR 4 million project to permanently pedestrianise it. Additionally, Cork is now set to transfer the Playful Paradigm Good Practice to more Irish cities, supported by the URBACT National Practice Transfer Initiative 2021-2022.
Participatory approach
The URBACT Local Group (ULG) brought Cork City Council together with public bodies and associations across health, education, culture and sports. The sense of shared ownership and entrepreneurial approach sparked unexpected opportunities and partnerships.
The ULG has evolved into a steering group called ‘Let’s Play Cork’ that has already started advocating for the concept of the ‘playful city’ to become a core objective of the City Development Plan and is also contributing to a ‘Manifesto of EU Playful Cities’.
What difference has it made
The Playful Paradigm Network has led to changes in attitude towards gaming and playing both in local, regional and national policy design and visioning, visible in new and fruitful partnerships between organizations.
Along the way Cork also learned to interject play into its interagency networks, allowing it to disseminate the core values and objectives of play. Partnering organizations subsequently incorporated play into their ways of working as well as to their services and events, engaging in new ways with the communities that they serve and reach. This has unlocked new forms of creativity to help tackle some of the societal challenges that every city faces.
Transferring the practice
Exchanges between Cork and the city of Udine were already in place before the Urbact Transfer network , namely through the World Health Organisation’s Healthy Cities network. But the URBACT Playful paradigm network unlocked the capacities to pragmatically experiment the approach of playing the city in a number of projects, whose ideas and creativity is tied to peer learning among the European cities.
Transnational meetings between network partners enabled participants from Cork to bring home specific ideas and skills. For example, representatives of the city library and an early childhood programme were able to visit a toy library in Paris, leading to adoption of a similar model in Cork. Another workshop, in Viana di Castelo (PT), gave the Cork local group the con dence and theoretical basis to create the new River Lee Placemaking network described above.
Emaildenise.cahill@hse.ieRef nid16271


